Tax Reports - The Tax Reports Setting
This setting is used to define the tax calculation formulae that will make up your custom reports. Each record in this setting contains a complete report definition.
To enter a new Tax Report definition or to edit an existing one, first open the 'Settings' list by clicking the [Settings] button in the Master Control panel or by selecting 'Settings' from the File menu. Double-click 'Tax Reports' in the list. The 'Tax Reports: Browse' window is displayed, showing all Tax Report definitions previously entered. Double-click a record in the list to edit it, or add a new record by clicking the [New] button in the Button Bar. When the record is complete, save it by clicking the [Save] button in the Button Bar or by clicking the close box and choosing to save changes. To close it without saving changes, click the close box.
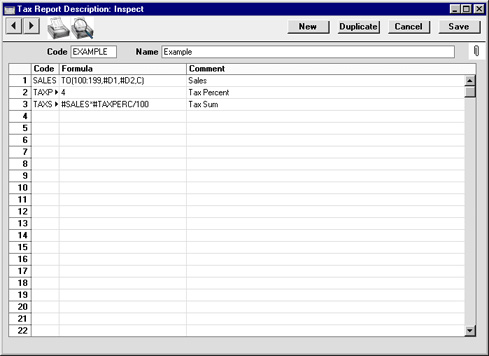
- Code
- The unique code identifying this Tax Report record (i.e. this set of report definitions).
- Name
- Enter a name for the Tax Report record as it will be shown in the 'Tax Records: Browse' window and the 'Paste Special' list.
Enter the report definitions (formulae) in the grid. Do not include any spaces in the formulae.
- Code
- A unique Code identifying each row.
- This Code can be used to refer to the row in other formulae, when it must be preceded by the # character (#SALES and #TAXPERC in row 3 of the illustration are examples, referring to rows 1 and 2 respectively). # is alt-3 on the UK Macintosh keyboard.
- Formula
- The formula used to calculate the value of this row.
- Comment
- The name of this row of the report, to be shown in the Tax Calculations report.
Several commands are available for use in the Formula field. They are not case sensitive.
TO(Account Code,Date 1,Date 2,Type)
This command returns the net change between Date 1 and Date 2 for the specified Account.
Use the Type parameter as follows:
- C
- returns the net change resulting from credit postings to the specified Account
- D
- returns the net change resulting from debit postings to the specified Account
- A
- returns the overall net change (Debit - Credit)
Some examples of the use of this command are as follows:
- TO(100,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,C)
- Returns the sum of the credit postings to Account 100 for the year 2002.
- TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A)
- Returns the sum of the net changes in Accounts 100 to 1999 for the year 2002. The Accounts used are determined using an alpha sort, rather than a numeric one. Thus Account 1000001 will be included in the example range, while Account 200 will not.
- -TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A)
- As the previous example, but the sign of the final figure is changed. This is useful when displaying figures for sales, which are stored as negative figures in Hansa. Prefixing the TO command with a minus sign will cause sales to be displayed as positive figures in the report.
OTO(Object Code,Account Code,Date 1,Date 2,Type)
This command is similar to TO, but in calculating the net change during the period for the specified Account, only postings with the specified Object Code are taken into account.
The reference to the Object Code is case sensitive. For example:
- OTO(A,100,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,C)
- Returns the sum of the credit postings with Object A to Account 100 for the year 2002. Credit postings with Object a will not be included.
TO2(Account Code 1,Account Code 2,Date 1,Date 2)
This command returns the net change between two Accounts (i.e. between two corresponding Accounts) between Date 1 and Date 2. For example:
- TO2(750,100,01/01/2002,31/12/2002)
- Returns the sum of the postings during the year 2002 where Account 750 is the debit Account and 100 is the corresponding credit Account.
- TO2(750,100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002)
- Returns the sum of the postings during the year 2002 where Account 750 is the debit Account and any Account between 100 and 1999 is the corresponding credit Account.
OTO2(Object Code,Account Code 1,Account Code 2,Date 1,Date 2)
This command is similar to TO2, but in calculating the net change between the corresponding Accounts, only double-sided postings where the specified Object Code is used on both sides are taken into account.
The reference to the Object Code is case sensitive.
BAL(Account Code,Date,Type)
This command returns the balance for the specified Account on the specified Date. It therefore differs from the TO command in that balances brought forward from previous periods are taken into account.
The command can return the sum of the balances of a range of Accounts in the same manner as the TO command: please refer to the description of the TO command above for examples.
OBAL(Object Code,Account Code,Date,Type)
This command is similar to BAL, but in calculating the balance for the specified Account on the specified date, only postings with the specified Object Code are taken into account.
ABS(expression)
This command returns the absolute (positive) value of the expression. The expression can be a hard-coded number or a formula using one of the Tax Report commands. For example:
- ABS(-1)
- Returns 1
- ABS(1)
- Returns 1
- ABS(TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A))
- Returns the sum of the net changes in the income Accounts 100 to 1999 for the year 2002, expressed as a positive figure. Balances for income Accounts are stored as negative figures in Hansa.
SIGN(expression)
This command returns the following:
- 1
- if the value of the expression is positive
- -1
- if the value of the expression is negative
- 0
- the value of the expression is zero
The expression can be a hard-coded number or a formula using one of the Tax Report commands. For example:
- SIGN(TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A))
- Returns -1 since the balances of income Accounts are negative
- SIGN(ABS(TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A)))
- Returns 1, since the ABS command expresses the balances of income Accounts as positive figures
ROUND(expression,number of decimal places)
This command returns the value of the expression rounded to the specified number of decimal places. The expression can be a hard-coded number or a formula using one of the Tax Report commands. For example:
- ROUND(1234.24,0)
- Returns 1234
- ROUND(1234.24,1)
- Returns 1234.2
- ROUND(1234.24,-2)
- Returns 1200
- ROUND(TO(100:1999,01/01/2002,31/12/2002,A),2)
- Returns the sum of the net changes in the income Accounts 100 to 1999 for the year 2002, rounded to two decimal places.
IF(expression, return 1, return 2)
This command returns the following:
- return 1
- if the value of the expression is positive or zero
- return 2
- if the value of the expression is negative
The expression, return 1 and return 2 can all be hard-coded numbers or formulae using one of the Tax Report commands. For example:
- IF(BAL(100,31/12/2002,A),1,-1)
- Returns 1 if BAL(100,31/12/2002,A) is positive or -1 if it is negative
Dates
Where a date is to be included in a formula, it can be hard-coded as in the examples above, or you can use one of the following variables:
- #D1
- The first date of the report period, as entered in the report or document specification window
- #D2
- The last date of the report period, as entered in the report or document specification window
- #D3
- The Previous Date, as entered in the report or document specification window
It is recommended that you use these variables, to ensure that your formulae can be used at any time without modification.
For example, to print the closing balance for Account 100 for the report period 1/1/2002:31/12/2002, you could hard-code the date in the formula as follows:
- BAL(100,01/12/2002,A)
Alternatively, you could take the date from the report period, as follows:
- BAL(100,#D2,A)
Unexpected Results
If a Tax Report record produces unexpected results and you are certain that the formulae are correct, the probable cause is that you are using the comma as the Decimal or Date Separator in the Date and Numeric Formats setting in the System module. As shown above, the comma is also used to separate the parameters in the formula commands. If you wish to continue using the comma as the Decimal or Date Separator, please refer to your local Hansa representative for a solution.
|
